The architectural design is based on a service-oriented structure that enables secure and flexible interaction between a custom Power BI visual, a Web API component, and an SQL Server instance. The goal is to perform interactive data operations directly from within Power BI—currently limited to creating and updating records. The DELETE function is not yet implemented but is already accounted for in the architecture.
cBI Focus Planner allows different deployment approaches. Some examples are:
- SaaS (Software-as-a-Service)
- Customer-Hosted Cloud Docker
- Customer-Hosted On-Premises Docker
- Customer-Hosted On-Premises IIS
- Hybrid
All of them share the same three core components that communicate with each other:
- Power BI (at least Pro subscription or Microsoft 365 with the appropriate license) with cBI Focus Planner Visual
- The customer’s SQL Server database
- The cBI Focus Planner Web API
Deployment Examples #
The cBI Focus Planner offers a flexible deployment architecture designed to meet diverse organizational needs and IT environments. Whether hosted in the cloud, on-premises, or in a hybrid setup, each deployment model ensures secure and efficient communication between Power BI, the cBI Focus Planner Web API, and the customer’s SQL Server database.
The following examples illustrate various deployment strategies—ranging from fully managed SaaS to Customer-hosted Docker and IIS configurations—highlighting the adaptability of the solution to different compliance, scalability, and data residency requirements.
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) #
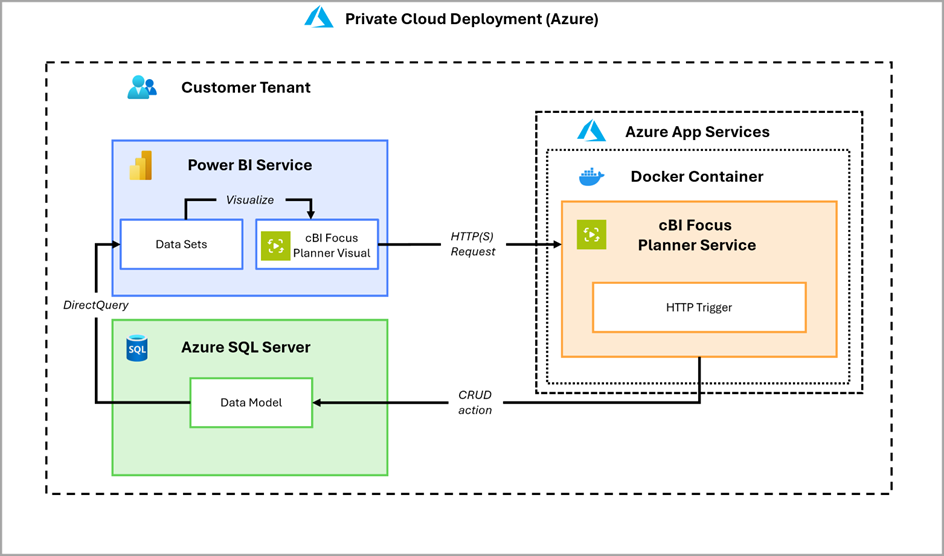
This is an example of the SaaS approach. At the core is the custom visual, cBI Focus Planner, embedded as a matrix visual in a Power BI report and serves as the user interface for capturing (planning) data. Developed using Microsoft’s official Power BI Visuals SDK, it allows users not only to visualize and consume data, but also to actively interact with the database. Through UI elements such as input fields or buttons, users can trigger actions that send HTTP requests to the Web API, cBI Focus Planner Service, which acts as middleware. These requests contain the necessary information to perform targeted database operations.
The cBI Focus Planner Service is hosted as a web service in the cBI Focus’ Azure tenant. Therefore, no additional installations are needed. This service serves as the central interface between the visual and the customer’s SQL Server database. It receives HTTP requests from the visual, handles authentication, and executes the corresponding SQL commands. The API is designed to be multi-tenant capable and can communicate with various SQL Server instances—regardless of the hosting environment (cloud or on-premises).
The SQL Server instance resides in the customer’s environment (in the customer’s Azure Tenant in the above example) and contains the relevant data structures and tables accessed by both Power BI and the Web API. The connection is established via dedicated SQL logins. The database user should have only the minimum necessary permissions to perform the required operations, ensuring a high level of security.
In the SaaS model, the cBI Focus Planner Web API is hosted in the cBI Focus Azure tenant. The custom visual, embedded in a Power BI report, serves as the user interface for planning and interacting with data. While the customer’s SQL Server database remains in their own cloud environment, only the data required for writeback operations is transmitted through the cBI Focus Planner Service. This service securely redirects requests to the target database using dedicated SQL logins with minimal permissions. No additional installations are required, and the architecture supports multi-tenant environments.
Customer-Hosted Cloud Docker #
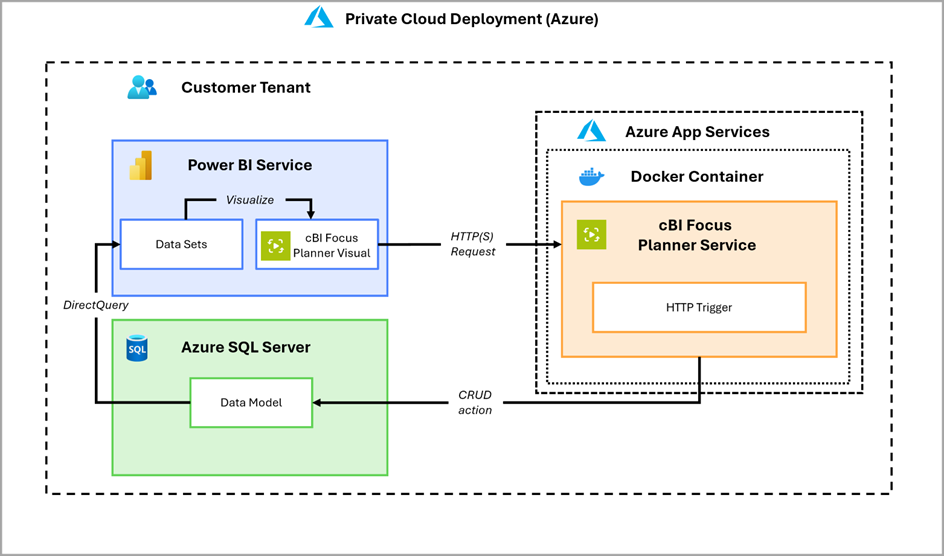
This model deploys the cBI Focus Planner Web API as a Docker container within the customer’s own cloud infrastructure (e.g., Azure, AWS, GCP). It offers full control over the hosting environment while maintaining scalability and isolation. All data remains within the customer’s cloud, ensuring compliance with internal policies and minimizing external data exposure.
Customer-Hosted On-Premises Docker #
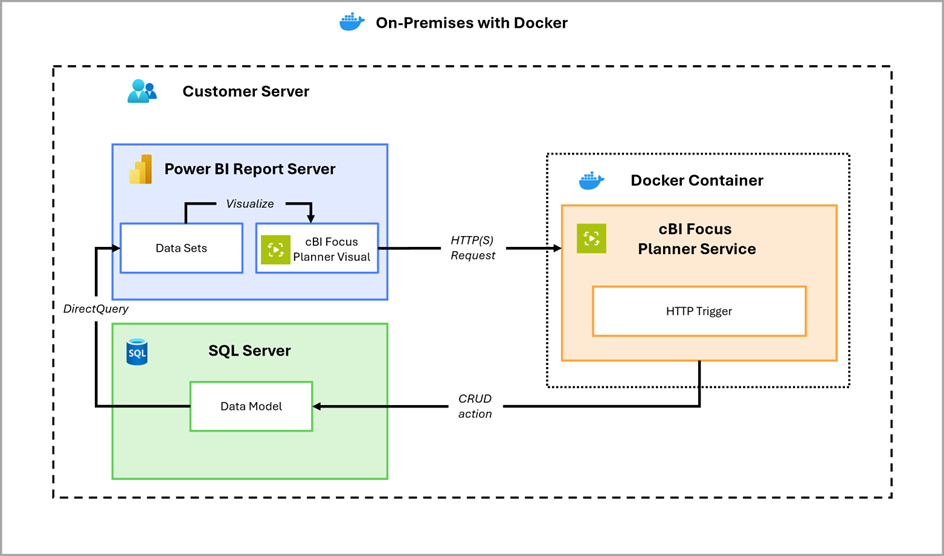
In this setup, the Web API runs in a Docker container on the customer’s internal infrastructure. It is ideal for organizations with strict data residency or compliance requirements. To enhance data privacy, this model can be paired with Power BI Report Server, allowing reports to be hosted and consumed entirely within the customer’s intranet. All data remains confined to the internal network.
Customer-Hosted On-Premises IIS #
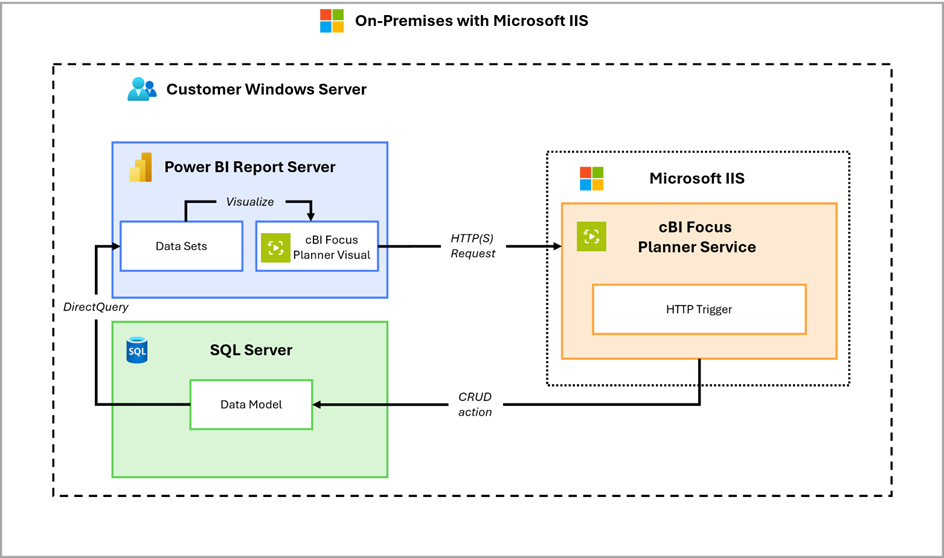
This traditional deployment hosts the Web API on a Windows Server using Internet Information Services (IIS). It is well-suited for environments standardized on Windows-based hosting. In addition to the benefits of the on-premises Docker model, this approach supports Windows Authentication via a Windows Service Account assigned to the IIS Application Pool. This enables integrated security for database access without requiring setting up SQL logins in the visual.
Hybrid (Cloud + On-Premises Docker) #
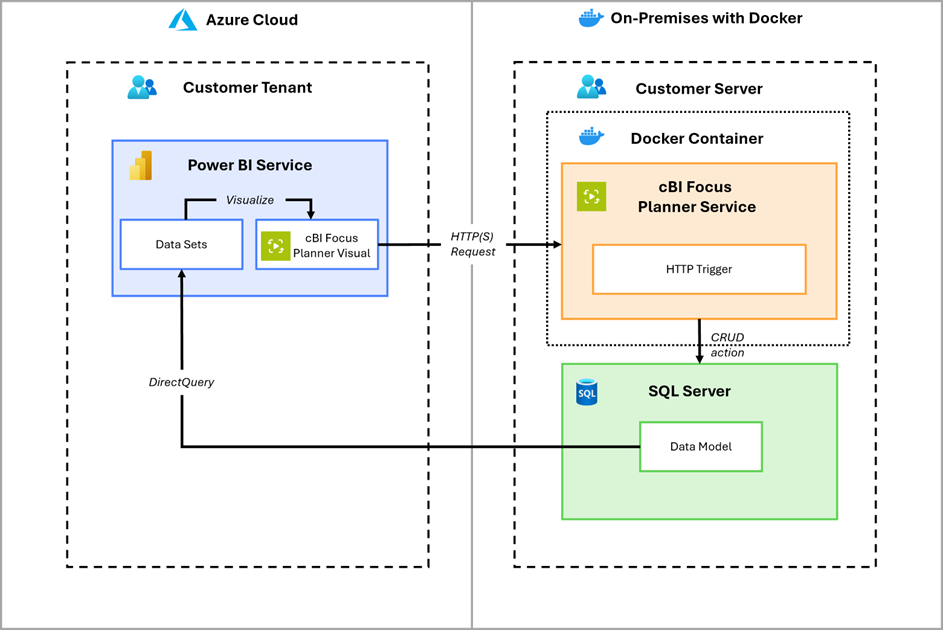
The hybrid model combines cloud-based Power BI services with an on-premises Docker deployment of the Web API. This allows organizations to leverage the scalability and accessibility of Power BI in the cloud while maintaining full control over sensitive data and backend processing within their internal infrastructure. A data gateway must be installed to enable secure communication between the Power BI Service and the on-premises SQL Server.
Authentication Flows for Data Writeback #
To ensure secure and efficient communication for the writeback process from the cBI Focus Planner visual to the underlying SQL Server database, multiple authentication flows are supported. Each method is designed to accommodate different deployment models, security policies, and administrative preferences. The following authentication strategies offer varying levels of granularity, ease of management, and integration with existing infrastructure.
SQL Server Authentication (User Login) #
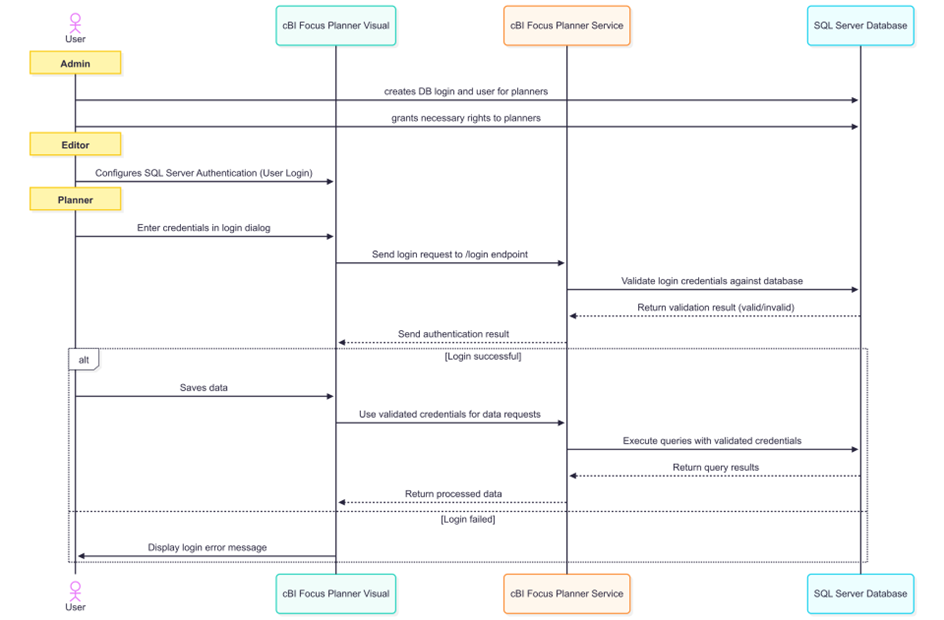
In this approach, each planner is assigned a dedicated SQL Server user account. The user logs in when launching the visual, enabling fine-grained access control at the database level.
While this method offers strong user-level security, it requires more administrative effort to manage individual accounts and credentials.
SQL Server Authentication (Proxy) #
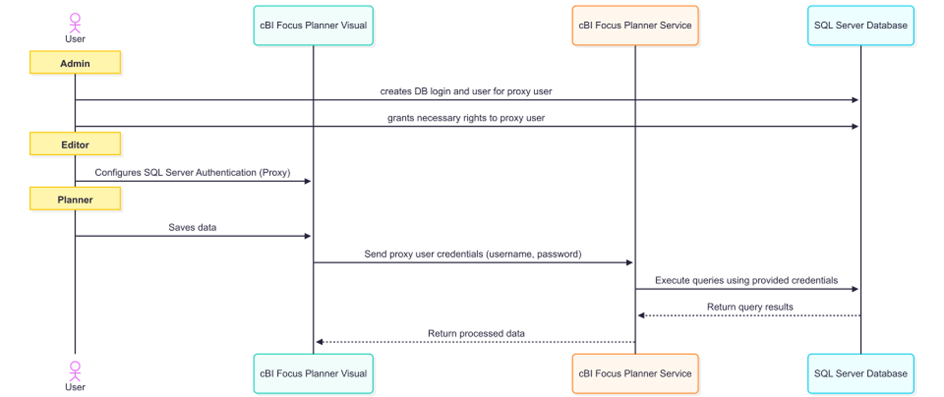
This method uses a single, fixed SQL Server proxy account to authenticate all planners. It simplifies user management by eliminating the need for individual SQL Server accounts and login prompts.
While access control is less granular, it significantly reduces administrative overhead and streamlines the user experience.
Windows Service Account Authentication #
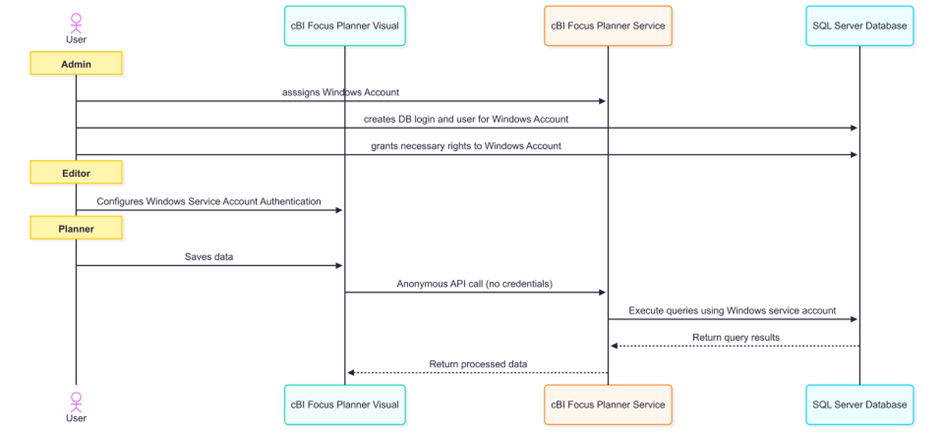
Available only in Customer-hosted IIS deployments, this method leverages Windows Authentication by assigning a Windows Service Account to the IIS Application Pool hosting the cBI Focus Planner Web API. All database interactions are performed under this service account. It offers similar benefits to the proxy approach, with even less configuration required in the visual, but demands additional setup on the infrastructure side.
Selection Criteria and Decision Matrix for Deployment Models #
Choosing the right deployment model for the cBI Focus Planner depends on a variety of factors, including infrastructure ownership, security requirements, IT capabilities, and integration preferences. The following decision matrix provides a comparative overview of each supported deployment option, helping stakeholders evaluate the trade-offs and select the most suitable configuration for their organizational needs.
| SaaS | Cloud Docker | OnPrem Docker | OnPrem IIS | Hybrid | |
| Infrastructure Ownership | cBI Focus (excluding DB) | Customer | Customer | Customer | Customer |
| Setup Complexity | Very Low | Medium | High | High | Medium-High |
| Security & Compliance | Medium | Medium | High | High | Medium |
| Power BI Connectivity | Direct | Direct | Direct | Direct | Requires Gateway |
| Windows Service Authentication | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Best For | Quick start, minimal IT overhead | Cloud-native teams with IT capacity | Regulated industries, full control | Windows-based IT environments | Mixed environments, sensitive data |




